Astronomers believe they may have found the first direct evidence of a new planet being born.
A dense disc of dust and gas has been spotted surrounding a young star called AB Aurigae, around 520 light years away from Earth.
Using the European Southern Observatory’s Very Large Telescope (VLT), located in Chile, the researchers observed a spiral structure with a “twist” near the centre, which suggests a new world may be in the process of forming. The swirling disc is one of the telltale signs of the star system being born in the constellation of Auriga, the scientists said.
Read more about exoplanets:
Dr Anthony Boccaletti, who led the study from the Observatoire de Paris, PSL University, France, said: “Thousands of exoplanets have been identified so far, but little is known about how they form.”
He added: “We need to observe very young systems to really capture the moment when planets form.”
Until now astronomers had been unable to take clear images of young discs to see these twists.
Dr Boccaletti and his team of astronomers used VLT’s Sphere instrument to take photos of AB Aurigae, which show “a stunning spiral of dust” caused by the baby planet trying to “kick” the gas.The same instrument was used in 2018 to take photos of another infant planet, thought to be just 5.4 million years old.
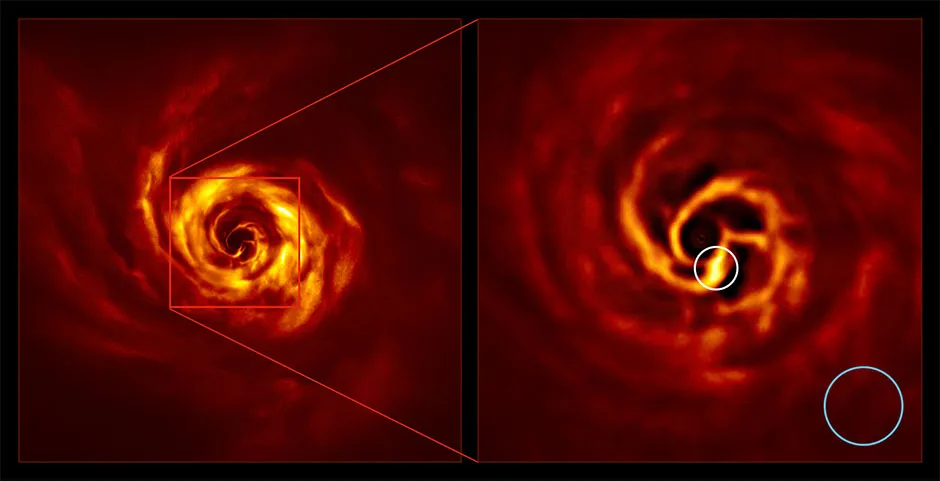
According Emmanuel Di Folco, of the Astrophysics Laboratory (LAB) of Bordeaux in France and one of the study authors, this so-called kicking phenomenon causes “disturbances in the disc in the form of a wave, somewhat like the wake of a boat on a lake”.
As the new planet rotates around AB Aurigae, it causes the surrounding gas and dust to be shaped into a spiral arm.The very bright yellow region near the centre of the spiral is the twist, which lies at about the same distance from the star as Neptune from the Sun.
Anne Dutrey, also at LAB and a study co-author, said: “The twist is expected from some theoretical models of planet formation.
“It corresponds to the connection of two spirals – one winding inwards of the planet’s orbit, the other expanding outwards – which join at the planet location. They allow gas and dust from the disc to accrete onto the forming planet and make it grow.”
The observations are reported in the journal Astronomy & Astrophysics.
What does it mean if an exoplanet is 'habitable'?
All forms of life that we know of depend on one critical component: liquid water. So, in the search for life, astronomers focus on planets where liquid water could exist, which they call 'habitable'.
Every star has a 'habitable zone', also called the 'Goldilocks zone', where it is not too hot and not too cold. A planet in the habitable zone gets the right amount of energy from the star to support liquid water. Any closer in to the star and water would boil, and any further out and it would freeze.
However, this doesn't guarantee that liquid water would exist on a planet in the habitable zone. The planet's atmosphere could be too thick, raising the temperature even higher. And even if liquid water does exist on the planet, habitable doesn't mean inhabited.
Read more: