- Astronomers have detected the biggest explosion in the Universe since the Big Bang.
- A supermassive black hole released the energetic explosion over 240 million years ago.
- This discovery will be the first of many, astronomers believe.
The biggest explosion in the Universe since the Big Bang has been discovered by astronomers.
The blast came from a supermassive black hole at the centre of a galaxy hundreds of millions of light-years away.Scientists say it released five times more energy than the previous record holder.
Professor Melanie Johnston-Hollitt, from the Curtin University node of the International Centre for Radio Astronomy Research, said the event was extraordinarily energetic.“This is the most energetic outburst we have seen since the Big Bang,” she told the PA news agency.
Read more about black holes:
- Wormholes: Could we travel through a black hole into another galaxy?
- The M87 image will change our understanding of black holes, but why was the photo so hard to capture?
She added that the age of the outburst is between 240 and 400 million years, as radio properties suggest it must have happened at least 240 million years ago and optical data indicates the upper limit to the age is 400 million years.
Prof Johnston-Hollit explained: “We’ve seen outbursts in the centres of galaxies before but this one is really, really massive. But it happened very slowly – like an explosion in slow motion that took place over hundreds of millions of years.”
The explosion occurred in the Ophiuchus galaxy cluster, about 390 million light-years from Earth, and was so powerful it blasted a hole in the cluster plasma – the super-hot gas surrounding the black hole.
Lead author of the study Dr Simona Giacintucci, from the Naval Research Laboratory in America, said the blast was similar to the 1980 eruption of Mount St Helens, which ripped the top off the mountain.She added: “The difference is that you could fit 15 Milky Way galaxies in a row into the crater this eruption punched into the cluster’s hot gas.”
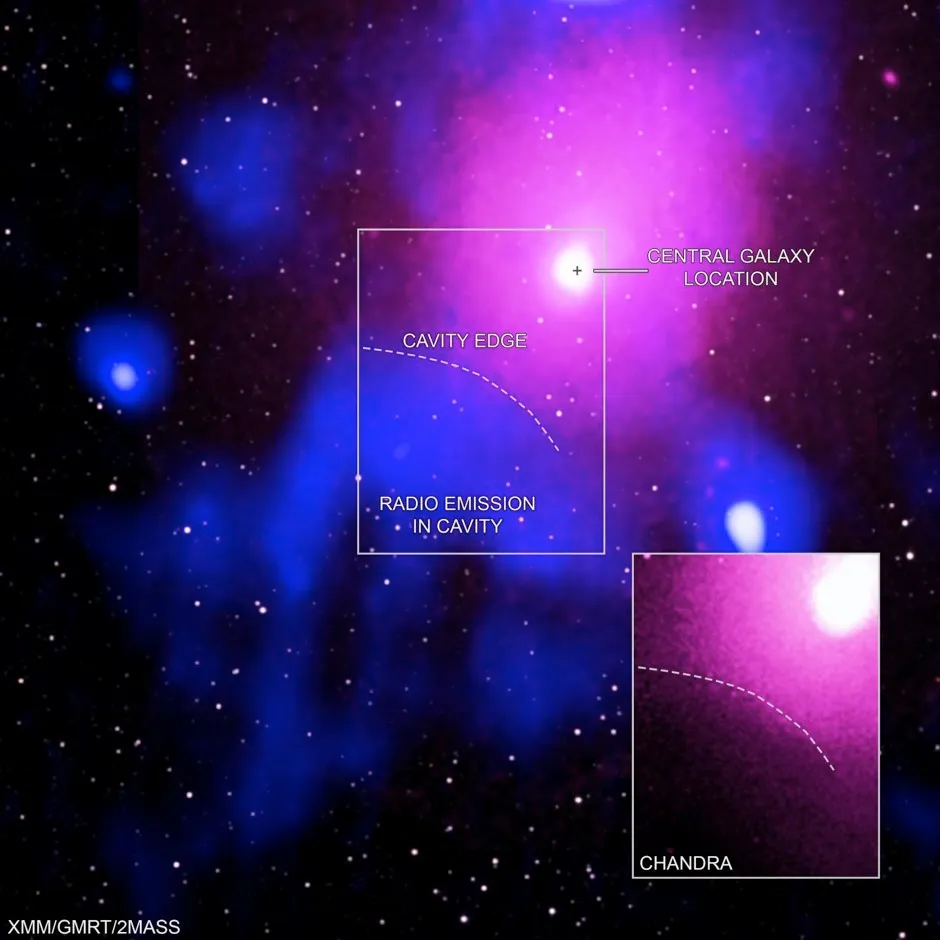
Professor Johnston-Hollitt said scientists initially dismissed that hole could have been caused by an energetic outburst, because it would have been too big.She explained: “People were sceptical because the size of outburst. But it really is that. The Universe is a weird place.”
Read more about the Big Bang:
Astronomers only realised what had happened when they looked at the Ophiuchus galaxy cluster with radio telescopes.“The radio data fit inside the X-rays like a hand in a glove,” said co-author Dr Maxim Markevitch, from NASA’s Goddard Space Flight Centre.
“This is the clincher that tells us an eruption of unprecedented size occurred here.”
The discovery was made using four telescopes; NASA’s Chandra X-ray Observatory, ESA’s XMM-Newton, the Murchison Widefield Array (MWA) in Western Australia and the Giant Metrewave Radio Telescope (GMRT) in India.
Professor Johnston-Hollitt said the finding is likely to be the first of many.“We made this discovery with Phase 1 of the MWA, when the telescope had 2,048 antennas pointed towards the sky,” she said.“We’re soon going to be gathering observations with 4,096 antennas, which should be 10 times more sensitive.
“I think that’s pretty exciting.”
The discovery is published in the Astrophysical Journal.
Reader Q&A: What’s the biggest gamma-ray burst ever recorded?
Asked by: C Osborne, South Wales
Gamma-ray bursts (GRBs) are extremely energetic flashes of radiation caused by the collapse of massive stars to form neutron stars or black holes. They are the most energetic events known in the Universe, but extremely rare.
The record for the most energetic is named GRB 130427A, which occurred on 27 April 2013. It was detected by many telescopes, on Earth and in space, and occurred in a galaxy in the constellation of Leo, about 3.8 billion light-years away. This is relatively nearby for a GRB, which explains why it was so bright. In fact, GRB 130427A was more than five times brighter than the previous record.
It’s the biggest explosion astronomers know about, after the Big Bang itself. If it had happened in our arm of the Milky Way, it would have destroyed all life on Earth.
Read more: