1. Skin
Average weight: 4,535g
Function: Protects against pathogens; provides insulation; synthesizes vitamin D; regulates temperature; provides sensation
2. Liver
Average weight: 1,560g
Function: Breaks down toxins; produces hormones, proteins and digestive biochemicals; regulates glycogen storage
3. Brain
Average weight: 1,500g
Function: Drives executive functions such as reasoning; coordinates responses to changes in environment
4. Lungs
Average weight: 1,300g
Function: Supplies oxygen to be distributed around the body; expels carbon dioxide that is created around the body
5. Heart
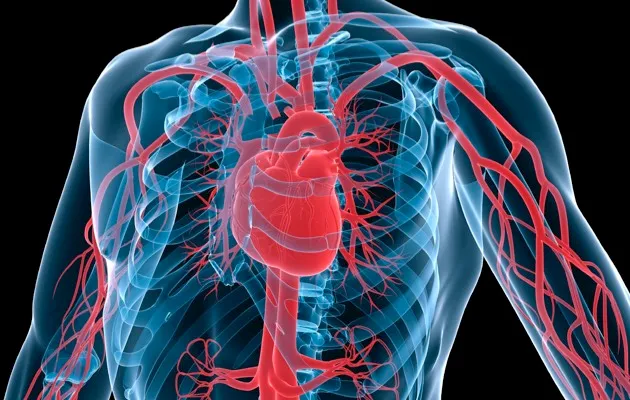
Average weight: 300g
Function: Pumps oxygenated blood from lungs around the body; pumps deoxygenated blood to the lungs
6. Kidneys
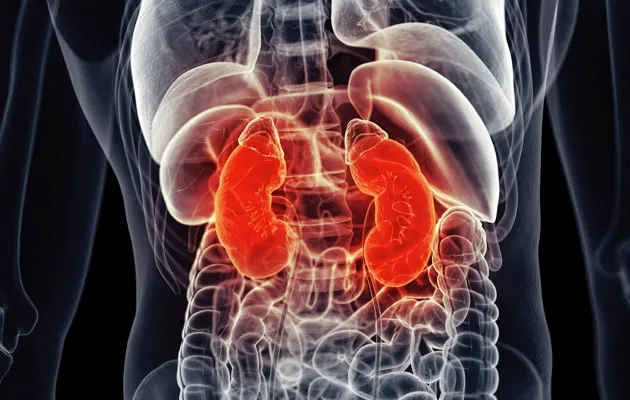
Average weight: 260g (pair)
Function: Remove waste products; regulate sodium and water retention; filter blood; produce urine and hormones
7. Spleen
Average weight: 175g
Function: Filters blood; holds a reserve supply of blood; recycles iron; synthesizes antibodies; removes bacteria
8. Pancreas
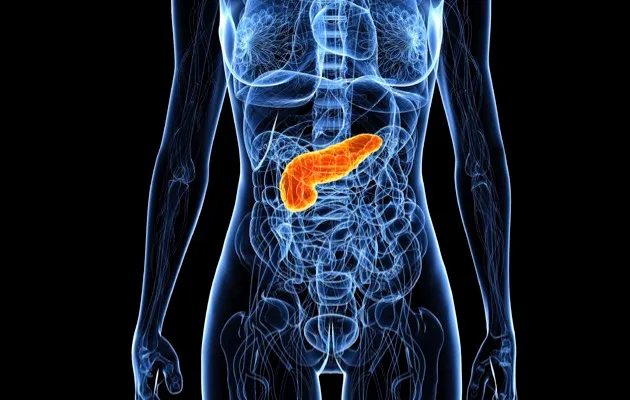
Average weight: 70g
Function: Produces insulin and glycogen; secretes enzymes that assist in the absorption of nutrients in the small intestine
9. Thyroid
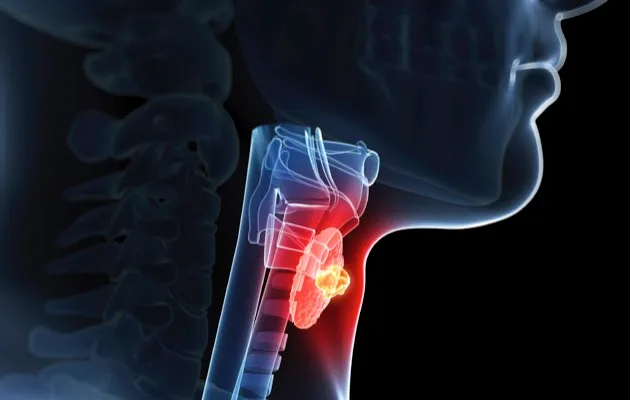
Average weight: 20g
Function: Controls body’s energy use; makes proteins; controls hormone sensitivity
10. Prostate gland
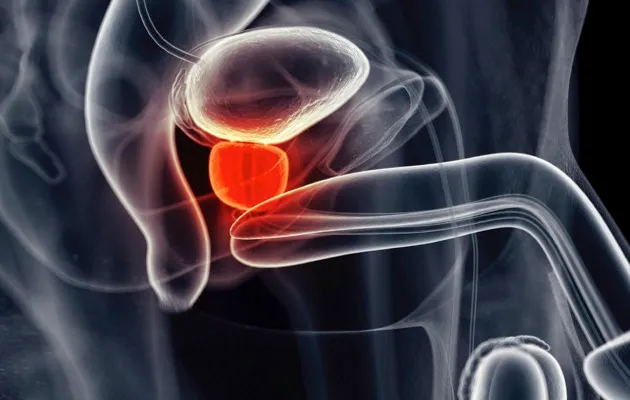
Average weight: 11g
Function: Secretes an alkaline fluid that constitutes 50-75 per cent of the volume of semen
Subscribe to BBC Focus magazine for fascinating new Q&As every month and follow @sciencefocusQA on Twitter for your daily dose of fun science facts.